es6
骚骚的reduce
每天进步一点点 • lopo1983 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 1588 次浏览 • 2018-07-05 02:04
accumulatorcurrentValuecurrentIndexarray
回调函数第一次执行时,accumulator?和currentValue的取值有两种情况:调用reduce时提供initialValue,accumulator取值为initialValue,currentValue取数组中的第一个值;没有提供?initialValue,accumulator取数组中的第一个值,currentValue取数组中的第二个值
?
计算某个字符出现的次数[...'abcdaabdcfggtre'].reduce((a,b)=>{a<strong>?a<strong>++:a<strong>=1;return a},{})[b][b]字母游戏[/b][/b]const anagrams = str => {
if (str.length <= 2) {
return str.length === 2 ? [str, str[1] + str[0]] : str;
}
return str.split("").reduce((acc, letter, i) => {
return acc.concat(anagrams(str.slice(0, i) + str.slice(i + 1)).map(val => letter + val));
}, );
}
anagrams("abc");[b][b]累加器[/b][/b]const sum = arr => arr.reduce((acc, val) => acc + val, 0);
sum([1, 2, 3]);[b][b]计数器[/b][/b]const countOccurrences = (arr, value) => arr.reduce((a, v) => v === value ? a + 1 : a + 0, 0);
countOccurrences([1, 2, 3, 2, 2, 5, 1], 1);[b][b]函数柯里化[/b][/b]const curry = (fn, arity = fn.length, ...args) =>
arity <= args.length ? fn(...args) : curry.bind(null, fn, arity, ...args);
curry(Math.pow)(2)(10);
curry(Math.min, 3)(10)(50)(2);
[b][b]通过判断函数的参数取得当前函数的length(当然也可以自己指定),如果所传的参数比当前参数少,则继续递归下面,同时储存上一次传递的参数。[/b][/b]
[b][b]数组扁平化[/b][/b]const deepFlatten = arr =>arr.reduce((a, v) => a.concat(Array.isArray(v) ? deepFlatten(v) : v), );
deepFlatten([1, [2, [3, 4, [5, 6]]]]);
[b][b]生成菲波列契数组[/b][/b]const fibonacci = n => Array(n).fill(0).reduce((acc, val, i) => acc.concat(i > 1 ? acc[i - 1] + acc[i - 2] : i), );
fibonacci(5);[b][b]pipe函数生成器[/b][/b]const pipe = (...funcs) => arg => funcs.reduce((acc, func) => func(acc), arg);
pipe(btoa, x => x.toUpperCase())("Test");
[b][b]通过对传递的参数进行函数加工,之后将加工之后的数据作为下一个函数的参数,这样层层传递下去。[/b][/b]
[b][b]compose函数生成器[/b][/b]const dispatch = action => {
console.log('action', action);
return action;
}
const middleware1 = dispatch => {
return action => {
console.log("middleware1");
const result = dispatch(action);
console.log("after middleware1");
return result;
}
}
const middleware2 = dispatch => {
return action => {
console.log("middleware2");
const result = dispatch(action);
console.log("after middleware2");
return result;
}
}
const middleware3 = dispatch => {
return action => {
console.log("middleware3");
const result = dispatch(action);
console.log("after middleware3");
return result;
}
}
const compose = middlewares => middlewares.reduce((a, b) => args => a(b(args)))
const middlewares = [middleware1, middleware2, middleware3];
const afterDispatch = compose(middlewares)(dispatch);
const testAction = arg => {
return { type: "TEST_ACTION", params: arg };
};
afterDispatch(testAction("1111"));[b][b]?
数据加工函数[/b][/b]const reducers = {
totalInEuros: (state, item) => {
return state.euros += item.price * 0.897424392;
},
totalInYen: (state, item) => {
return state.yens += item.price * 113.852;
}
};
const manageReducers = reducers => {
return (state, item) => {
return Object.keys(reducers).reduce((nextState, key) => {
reducers[key](state, item);
return state;
}, {})
}
}
const bigTotalPriceReducer = manageReducers(reducers);
const initialState = { euros: 0, yens: 0 };
const items = [{ price: 10 }, { price: 120 }, { price: 1000 }];
const totals = items.reduce(bigTotalPriceReducer, initialState);[b][b]对象空值判断[/b][/b]const get = (p, o) => p.reduce((xs, x) => (xs && xs[x] ? xs[x] : null), o);[b][b]分组[/b][/b]const groupBy = (arr, func) =>
arr.map(typeof func === 'function' ? func : val => val[func]).reduce((acc, val, i) => {
acc[val] = (acc[val] || ).concat(arr);
return acc;
}, {});
groupBy([6.1, 4.2, 6.3], Math.floor);
groupBy(['one', 'two', 'three'], 'length');[b][b]对象过滤[/b][/b]const pick = (obj, arr) =>
arr.reduce((acc, curr) => (curr in obj && (acc[curr] = obj[curr]), acc), {});
pick({ a: 1, b: '2', c: 3 }, ['a', 'c']);[b][b]promise顺序执行[/b][/b]const runPromisesInSeries = ps => ps.reduce((p, next) => p.then(next), Promise.resolve());
const delay = d => new Promise(r => setTimeout(r, d));
const print = args => new Promise(r => r(args));
runPromisesInSeries([() => delay(1000), () => delay(2000), () => print('hello')])[b][b]排序函数[/b][/b]const orderBy = (arr, props, orders) =>
[...arr].sort((a, b) =>
props.reduce((acc, prop, i) => {
if (acc === 0) {
const [p1, p2] = orders && orders === 'desc' ? [b[prop], a[prop]] : [a[prop], b[prop]];
acc = p1 > p2 ? 1 : p1 < p2 ? -1 : 0;
}
return acc;
}, 0)
);
const users = [{ name: 'fred', age: 48 }, { name: 'barney', age: 36 }, { name: 'fly', age: 26 }];
orderBy(users, ['name', 'age'], ['asc', 'desc']);
orderBy(users, ['name', 'age']);[b][b]快速选择器[/b][/b]const select = (from, selector) =>
selector.split('.').reduce((prev, cur) => prev && prev[cur], from);
const obj = { selector: { to: { val: 'val to select' } } };
select(obj, 'selector.to.val'); 查看全部
arr.reduce(callback[, initialValue])reduce为数组中的每一个元素依次执行callback函数,不包括数组中被删除或从未被赋值的元素,接受四个参数:- accumulator
- currentValue
- currentIndex
- array
回调函数第一次执行时,accumulator?和currentValue的取值有两种情况:调用reduce时提供initialValue,accumulator取值为initialValue,currentValue取数组中的第一个值;没有提供?initialValue,accumulator取数组中的第一个值,currentValue取数组中的第二个值
?
计算某个字符出现的次数
[...'abcdaabdcfggtre'].reduce((a,b)=>{a<strong>?a<strong>++:a<strong>=1;return a},{})[b][b]字母游戏[/b][/b]const anagrams = str => {
if (str.length <= 2) {
return str.length === 2 ? [str, str[1] + str[0]] : str;
}
return str.split("").reduce((acc, letter, i) => {
return acc.concat(anagrams(str.slice(0, i) + str.slice(i + 1)).map(val => letter + val));
}, );
}
anagrams("abc");[b][b]累加器[/b][/b]const sum = arr => arr.reduce((acc, val) => acc + val, 0);[b][b]计数器[/b][/b]
sum([1, 2, 3]);
const countOccurrences = (arr, value) => arr.reduce((a, v) => v === value ? a + 1 : a + 0, 0);[b][b]函数柯里化[/b][/b]
countOccurrences([1, 2, 3, 2, 2, 5, 1], 1);
const curry = (fn, arity = fn.length, ...args) =>
arity <= args.length ? fn(...args) : curry.bind(null, fn, arity, ...args);
curry(Math.pow)(2)(10);
curry(Math.min, 3)(10)(50)(2);
[b][b]通过判断函数的参数取得当前函数的length(当然也可以自己指定),如果所传的参数比当前参数少,则继续递归下面,同时储存上一次传递的参数。[/b][/b]
[b][b]数组扁平化[/b][/b]
const deepFlatten = arr =>arr.reduce((a, v) => a.concat(Array.isArray(v) ? deepFlatten(v) : v), );
deepFlatten([1, [2, [3, 4, [5, 6]]]]);
[b][b]生成菲波列契数组[/b][/b]
const fibonacci = n => Array(n).fill(0).reduce((acc, val, i) => acc.concat(i > 1 ? acc[i - 1] + acc[i - 2] : i), );[b][b]pipe函数生成器[/b][/b]
fibonacci(5);
const pipe = (...funcs) => arg => funcs.reduce((acc, func) => func(acc), arg);
pipe(btoa, x => x.toUpperCase())("Test");
[b][b]通过对传递的参数进行函数加工,之后将加工之后的数据作为下一个函数的参数,这样层层传递下去。[/b][/b]
[b][b]compose函数生成器[/b][/b]
const dispatch = action => {
console.log('action', action);
return action;
}
const middleware1 = dispatch => {
return action => {
console.log("middleware1");
const result = dispatch(action);
console.log("after middleware1");
return result;
}
}
const middleware2 = dispatch => {
return action => {
console.log("middleware2");
const result = dispatch(action);
console.log("after middleware2");
return result;
}
}
const middleware3 = dispatch => {
return action => {
console.log("middleware3");
const result = dispatch(action);
console.log("after middleware3");
return result;
}
}
const compose = middlewares => middlewares.reduce((a, b) => args => a(b(args)))
const middlewares = [middleware1, middleware2, middleware3];
const afterDispatch = compose(middlewares)(dispatch);
const testAction = arg => {
return { type: "TEST_ACTION", params: arg };
};
afterDispatch(testAction("1111"));[b][b]?数据加工函数[/b][/b]
const reducers = {
totalInEuros: (state, item) => {
return state.euros += item.price * 0.897424392;
},
totalInYen: (state, item) => {
return state.yens += item.price * 113.852;
}
};
const manageReducers = reducers => {
return (state, item) => {
return Object.keys(reducers).reduce((nextState, key) => {
reducers[key](state, item);
return state;
}, {})
}
}
const bigTotalPriceReducer = manageReducers(reducers);
const initialState = { euros: 0, yens: 0 };
const items = [{ price: 10 }, { price: 120 }, { price: 1000 }];
const totals = items.reduce(bigTotalPriceReducer, initialState);[b][b]对象空值判断[/b][/b]const get = (p, o) => p.reduce((xs, x) => (xs && xs[x] ? xs[x] : null), o);[b][b]分组[/b][/b]
const groupBy = (arr, func) =>[b][b]对象过滤[/b][/b]
arr.map(typeof func === 'function' ? func : val => val[func]).reduce((acc, val, i) => {
acc[val] = (acc[val] || ).concat(arr);
return acc;
}, {});
groupBy([6.1, 4.2, 6.3], Math.floor);
groupBy(['one', 'two', 'three'], 'length');
const pick = (obj, arr) =>[b][b]promise顺序执行[/b][/b]
arr.reduce((acc, curr) => (curr in obj && (acc[curr] = obj[curr]), acc), {});
pick({ a: 1, b: '2', c: 3 }, ['a', 'c']);
const runPromisesInSeries = ps => ps.reduce((p, next) => p.then(next), Promise.resolve());[b][b]排序函数[/b][/b]
const delay = d => new Promise(r => setTimeout(r, d));
const print = args => new Promise(r => r(args));
runPromisesInSeries([() => delay(1000), () => delay(2000), () => print('hello')])
const orderBy = (arr, props, orders) =>[b][b]快速选择器[/b][/b]
[...arr].sort((a, b) =>
props.reduce((acc, prop, i) => {
if (acc === 0) {
const [p1, p2] = orders && orders === 'desc' ? [b[prop], a[prop]] : [a[prop], b[prop]];
acc = p1 > p2 ? 1 : p1 < p2 ? -1 : 0;
}
return acc;
}, 0)
);
const users = [{ name: 'fred', age: 48 }, { name: 'barney', age: 36 }, { name: 'fly', age: 26 }];
orderBy(users, ['name', 'age'], ['asc', 'desc']);
orderBy(users, ['name', 'age']);
const select = (from, selector) =>
selector.split('.').reduce((prev, cur) => prev && prev[cur], from);
const obj = { selector: { to: { val: 'val to select' } } };
select(obj, 'selector.to.val');
JS 线树互转(es6)
每天进步一点点 • lopo1983 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 1742 次浏览 • 2018-07-01 12:09
菜单或者分类等业务场景时,每个顶级节点的parentId约定为0,当存在多个顶级节点,显得不是一个完整的树。所以在这类特殊情况下,我们需要构造一个顶级节点。将菜单或者分类的原有顶级节点存储至该节点的children中。 所以最后约定顶级节点如下。
root = null || {
id: 0,
parentId: null,
children: [node1, node2, ...],
}
线性转树形:function listConvertTree(list) {
let root = null;
if (list && list.length) {
root = { id: 0, parentId: null, children:};
const group = {};
for (let index = 0; index < list.length; index += 1) {
if (list[index].parentId !== null && list[index].parentId !== undefined) {
if (!group[list[index].parentId]) {
group[list[index].parentId] = ;
}
group[list[index].parentId].push(list[index]);
}
}
const queue = ;
queue.push(root);
while (queue.length) {
const node = queue.shift();
node.children = group[node.id] && group[node.id].length ? group[node.id] : null;
if (node.children) {
queue.push(...node.children);
}
}
}
return root;
}树形转线性:function treeConvertList(root) {
const list = ;
if (root) {
const Root = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(root));
const queue = ;
queue.push(Root);
while (queue.length) {
const node = queue.shift();
if (node.children && node.children.length) {
queue.push(...node.children);
}
delete node.children;
if (node.parentId !== null && node.parentId !== undefined) {
list.push(node);
}
}
}
return list;
} 查看全部
菜单或者分类等业务场景时,每个顶级节点的parentId约定为0,当存在多个顶级节点,显得不是一个完整的树。所以在这类特殊情况下,我们需要构造一个顶级节点。将菜单或者分类的原有顶级节点存储至该节点的children中。 所以最后约定顶级节点如下。
root = null || {
id: 0,
parentId: null,
children: [node1, node2, ...],
}
线性转树形:function listConvertTree(list) {
let root = null;
if (list && list.length) {
root = { id: 0, parentId: null, children:};
const group = {};
for (let index = 0; index < list.length; index += 1) {
if (list[index].parentId !== null && list[index].parentId !== undefined) {
if (!group[list[index].parentId]) {
group[list[index].parentId] = ;
}
group[list[index].parentId].push(list[index]);
}
}
const queue = ;
queue.push(root);
while (queue.length) {
const node = queue.shift();
node.children = group[node.id] && group[node.id].length ? group[node.id] : null;
if (node.children) {
queue.push(...node.children);
}
}
}
return root;
}树形转线性:function treeConvertList(root) {
const list = ;
if (root) {
const Root = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(root));
const queue = ;
queue.push(Root);
while (queue.length) {
const node = queue.shift();
if (node.children && node.children.length) {
queue.push(...node.children);
}
delete node.children;
if (node.parentId !== null && node.parentId !== undefined) {
list.push(node);
}
}
}
return list;
} 关于柯里化 curry
每天进步一点点 • lopo1983 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 1713 次浏览 • 2018-06-16 02:37
多亏了ES6,减少了不少阔怕的return,先上李子再扯蛋const add=>(x,y)=>x+y; //一般套路
add(1,2);const addcurry = a=>b=>a+b;//curry套路套路套路
addcurry(1)(2);
// 写下面的代码方便大家理解
var addcurry = function(a){
return function(b){
return b+a
}
}
截图很明显,一下下就明白了,这尼玛就是函数式编程里面的吉娃娃嘛,对 返回的就是一个函数,第一次输入值是返回一个函数,第二次的值作为了他的参数,就是这样 喵!嗷呜。。。。。对了,这里涉及了面试逼问的 闭包!!
是不是觉得 我靠 贼吉尔简单哇!
下面给大家copy 一个最近项目用到的一个李子,这个李子有点酸 是node下面用的?(虽然PHP是世界上最好的语言,总觉得自己可以玩node,结果还是愉快的使用了express-generator,对没错,我的理想还是做一名FBI纪录片摄影记者,侧重点是关注亚麻种植户的疾苦)。但是意思都差球不多 无太多的区别。const client = new AipNlp(...aipconf);
//
const AIPFC = (res) => async(aipfn) => {
const DATA = Object.assign({}, BACKJSON);
let result;
try {
result = await aipfn;
} catch (error) {
result = error
}
res.json(Object.assign(DATA, { data: result })).end();
};
exports.lexer = (req, res) => {
let aipfc = AIPFC(res);
aipfc(client.lexer(req.body.texts));
}前面的废话讲完了 先来说些柯里化 或涉及的一些基础术语
一、一元函数
接收一个参数的函数就叫一元函数(对对对 就是那种绿色的)const fn = (x) => x二、二元函数
接收连个参数的函数就叫二元函数(两张绿色的)const fn = (x,y) = > x+y
三、便餐函数
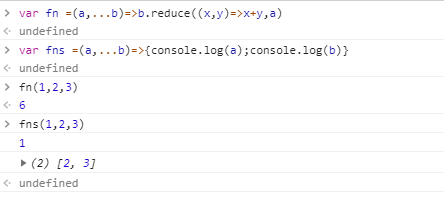
参数不固定的函数,es6之前用arguments来捕获,es6 可以用结构来获取const fn =(a,...b)=>b.reduce((x,y)=>x+y,a)
这些东西懂的可以忽略或者拍砖 标榜语言不准确的地方,谢谢
很多的函数库里面有会有curry这个函数 比如loash _.curry
下面我简单的来实现一个将多参数 变成一元的函数const add = (a,b)=>a+b;
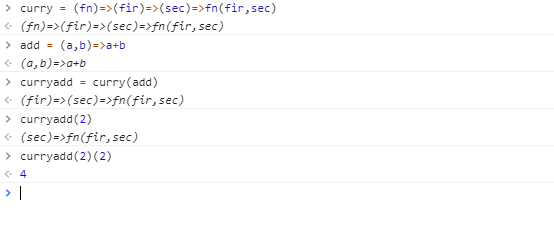
const curry = (fn)=>(fir)=>(sec)=>fn(fir,sec);
写了那么多东西,你肯定要说,这有屁用啊,屁用都没有,我什么要拆开他,老子的用户都是16核,16G的高端电脑,好好,说个吉娃娃,下面继续李子发起走,我们慢慢的玩上去,来波澳门赌场,澳门皇家赌场开业了。。。。扑哧
假如,我是说假如我们要创建一个列表 有点那么小规律的列表 list2 list3 list4等等
我们先暂时用这来试试const list2 = y=>2*y;
const list3 = y=>3*y;
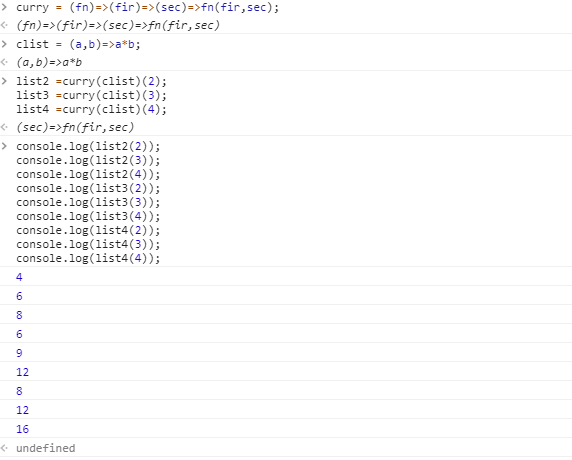
const list4 = y=>4*y再看看 尼玛 有规律的 来来来 改一版const clist = (a,b)=>a*b;
//
clist(2,2)
clist(2,3)
clist(2,4)
//拿东北的话来说 有一个姓铁的老大爷掉毛了(老铁没毛病);
继续骚起走,李子继续挥泪大甩卖,老板娘除外;const list2 =curry(clist)(2);
const list3 =curry(clist)(3);
const list4 =curry(clist)(4);
console.log(list2(2));
console.log(list2(3));
console.log(list2(4));
console.log(list3(2));
console.log(list3(3));
console.log(list3(4));
console.log(list4(2));
console.log(list4(3));
console.log(list4(4));
查看全部
函数 一等公民 ,越简单的函数越快,把一个复杂的函数打散成多个简单的小函数来执行,能增加执行的速度喝效率,和复用性?。在很多的js大牛的博客上肯定能找到许多的关于这个几把万一二的一些文章喝装13套路的文章,大多数都是互相的复制粘贴之流。简单的说柯里化就是把一个多参函数转换成嵌套的一元函数(毕竟一元最牛逼,因为脸都是绿的)。扯到柯里化 肯定就要继续再扯其他的反柯里化 偏函数 之类的 ,那个以后又空了再装逼。
多亏了ES6,减少了不少阔怕的return,先上李子再扯蛋
const add=>(x,y)=>x+y; //一般套路
add(1,2);
const addcurry = a=>b=>a+b;//curry套路套路套路
addcurry(1)(2);
// 写下面的代码方便大家理解
var addcurry = function(a){
return function(b){
return b+a
}
}
截图很明显,一下下就明白了,这尼玛就是函数式编程里面的吉娃娃嘛,对 返回的就是一个函数,第一次输入值是返回一个函数,第二次的值作为了他的参数,就是这样 喵!嗷呜。。。。。对了,这里涉及了面试逼问的 闭包!!
是不是觉得 我靠 贼吉尔简单哇!
下面给大家copy 一个最近项目用到的一个李子,这个李子有点酸 是node下面用的?(虽然PHP是世界上最好的语言,总觉得自己可以玩node,结果还是愉快的使用了express-generator,对没错,我的理想还是做一名FBI纪录片摄影记者,侧重点是关注亚麻种植户的疾苦)。但是意思都差球不多 无太多的区别。
const client = new AipNlp(...aipconf);前面的废话讲完了 先来说些柯里化 或涉及的一些基础术语
//
const AIPFC = (res) => async(aipfn) => {
const DATA = Object.assign({}, BACKJSON);
let result;
try {
result = await aipfn;
} catch (error) {
result = error
}
res.json(Object.assign(DATA, { data: result })).end();
};
exports.lexer = (req, res) => {
let aipfc = AIPFC(res);
aipfc(client.lexer(req.body.texts));
}
一、一元函数
接收一个参数的函数就叫一元函数(对对对 就是那种绿色的)
const fn = (x) => x二、二元函数
接收连个参数的函数就叫二元函数(两张绿色的)
const fn = (x,y) = > x+y
三、便餐函数
参数不固定的函数,es6之前用arguments来捕获,es6 可以用结构来获取
const fn =(a,...b)=>b.reduce((x,y)=>x+y,a)
这些东西懂的可以忽略或者拍砖 标榜语言不准确的地方,谢谢
很多的函数库里面有会有curry这个函数 比如loash _.curry
下面我简单的来实现一个将多参数 变成一元的函数
const add = (a,b)=>a+b;
const curry = (fn)=>(fir)=>(sec)=>fn(fir,sec);
写了那么多东西,你肯定要说,这有屁用啊,屁用都没有,我什么要拆开他,老子的用户都是16核,16G的高端电脑,好好,说个吉娃娃,下面继续李子发起走,我们慢慢的玩上去,来波澳门赌场,澳门皇家赌场开业了。。。。扑哧
假如,我是说假如我们要创建一个列表 有点那么小规律的列表 list2 list3 list4等等
我们先暂时用这来试试
const list2 = y=>2*y;再看看 尼玛 有规律的 来来来 改一版
const list3 = y=>3*y;
const list4 = y=>4*y
const clist = (a,b)=>a*b;拿东北的话来说 有一个姓铁的老大爷掉毛了(老铁没毛病);
//
clist(2,2)
clist(2,3)
clist(2,4)
//
继续骚起走,李子继续挥泪大甩卖,老板娘除外;
const list2 =curry(clist)(2);
const list3 =curry(clist)(3);
const list4 =curry(clist)(4);
console.log(list2(2));
console.log(list2(3));
console.log(list2(4));
console.log(list3(2));
console.log(list3(3));
console.log(list3(4));
console.log(list4(2));
console.log(list4(3));
console.log(list4(4));
43 位随机码 生成(0~9 A~Z a~z) 可定义位数(位数可随机)
javascript/jQuery • lopo1983 发表了文章 • 2 个评论 • 1466 次浏览 • 2017-04-22 16:20
randomStr: (randomFlag, min, max) => {
let str = "",
range = min,
arr = ['0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z', 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'M', 'N', 'O', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U', 'V', 'W', 'X', 'Y', 'Z'];
if(randomFlag) {
range = Math.round(Math.random() * (max - min)) + min;
}
for(let i = 0; i < range; i++) {
let pos = Math.round(Math.random() * (arr.length - 1));
str += arr[pos];
}
return str;
} 查看全部
//43位随机串 是否指定位数 最小位数 最大位数 (false 43)43位随机
randomStr: (randomFlag, min, max) => {
let str = "",
range = min,
arr = ['0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z', 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'M', 'N', 'O', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U', 'V', 'W', 'X', 'Y', 'Z'];
if(randomFlag) {
range = Math.round(Math.random() * (max - min)) + min;
}
for(let i = 0; i < range; i++) {
let pos = Math.round(Math.random() * (arr.length - 1));
str += arr[pos];
}
return str;
}
vue 滚动到底部
VUE • lopo1983 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 3090 次浏览 • 2017-04-13 03:04
datadata() {
return {
userMsg:
}
}
?
?
methodsgoBottom(e) {
e.scrollTop = e.scrollHeight
}mounted(如果需要进入就滚动)mounted: function() {
this.$nextTick(function() {
let e = this.$refs.chatbox;
this.goBottom(e);
})
}
watch(如果响应)watch: {
userMsg() {
this.$nextTick(() => {
let e = this.$refs.chatbox;
this.goBottom(e);
})
}
}?
?
<-------------------------------------------------邪恶分割线------------------------------------------------>
?
?
以上的代码完全可忽略 因为出现了 邪恶分割线
?
CSS3 FLEX 布局解决display: flex;
flex-flow: column-reverse;
align-items: baseline; 查看全部
<div class="mix" ref="chatbox">....</div>
data
data() {
return {
userMsg:
}
}?
?
methods
goBottom(e) {
e.scrollTop = e.scrollHeight
}mounted(如果需要进入就滚动)mounted: function() {
this.$nextTick(function() {
let e = this.$refs.chatbox;
this.goBottom(e);
})
}watch(如果响应)
watch: {
userMsg() {
this.$nextTick(() => {
let e = this.$refs.chatbox;
this.goBottom(e);
})
}
}??
<-------------------------------------------------邪恶分割线------------------------------------------------>
?
?
以上的代码完全可忽略 因为出现了 邪恶分割线
?
CSS3 FLEX 布局解决
display: flex;
flex-flow: column-reverse;
align-items: baseline;
骚骚的reduce
每天进步一点点 • lopo1983 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 1588 次浏览 • 2018-07-05 02:04
accumulatorcurrentValuecurrentIndexarray
回调函数第一次执行时,accumulator?和currentValue的取值有两种情况:调用reduce时提供initialValue,accumulator取值为initialValue,currentValue取数组中的第一个值;没有提供?initialValue,accumulator取数组中的第一个值,currentValue取数组中的第二个值
?
计算某个字符出现的次数[...'abcdaabdcfggtre'].reduce((a,b)=>{a<strong>?a<strong>++:a<strong>=1;return a},{})[b][b]字母游戏[/b][/b]const anagrams = str => {
if (str.length <= 2) {
return str.length === 2 ? [str, str[1] + str[0]] : str;
}
return str.split("").reduce((acc, letter, i) => {
return acc.concat(anagrams(str.slice(0, i) + str.slice(i + 1)).map(val => letter + val));
}, );
}
anagrams("abc");[b][b]累加器[/b][/b]const sum = arr => arr.reduce((acc, val) => acc + val, 0);
sum([1, 2, 3]);[b][b]计数器[/b][/b]const countOccurrences = (arr, value) => arr.reduce((a, v) => v === value ? a + 1 : a + 0, 0);
countOccurrences([1, 2, 3, 2, 2, 5, 1], 1);[b][b]函数柯里化[/b][/b]const curry = (fn, arity = fn.length, ...args) =>
arity <= args.length ? fn(...args) : curry.bind(null, fn, arity, ...args);
curry(Math.pow)(2)(10);
curry(Math.min, 3)(10)(50)(2);
[b][b]通过判断函数的参数取得当前函数的length(当然也可以自己指定),如果所传的参数比当前参数少,则继续递归下面,同时储存上一次传递的参数。[/b][/b]
[b][b]数组扁平化[/b][/b]const deepFlatten = arr =>arr.reduce((a, v) => a.concat(Array.isArray(v) ? deepFlatten(v) : v), );
deepFlatten([1, [2, [3, 4, [5, 6]]]]);
[b][b]生成菲波列契数组[/b][/b]const fibonacci = n => Array(n).fill(0).reduce((acc, val, i) => acc.concat(i > 1 ? acc[i - 1] + acc[i - 2] : i), );
fibonacci(5);[b][b]pipe函数生成器[/b][/b]const pipe = (...funcs) => arg => funcs.reduce((acc, func) => func(acc), arg);
pipe(btoa, x => x.toUpperCase())("Test");
[b][b]通过对传递的参数进行函数加工,之后将加工之后的数据作为下一个函数的参数,这样层层传递下去。[/b][/b]
[b][b]compose函数生成器[/b][/b]const dispatch = action => {
console.log('action', action);
return action;
}
const middleware1 = dispatch => {
return action => {
console.log("middleware1");
const result = dispatch(action);
console.log("after middleware1");
return result;
}
}
const middleware2 = dispatch => {
return action => {
console.log("middleware2");
const result = dispatch(action);
console.log("after middleware2");
return result;
}
}
const middleware3 = dispatch => {
return action => {
console.log("middleware3");
const result = dispatch(action);
console.log("after middleware3");
return result;
}
}
const compose = middlewares => middlewares.reduce((a, b) => args => a(b(args)))
const middlewares = [middleware1, middleware2, middleware3];
const afterDispatch = compose(middlewares)(dispatch);
const testAction = arg => {
return { type: "TEST_ACTION", params: arg };
};
afterDispatch(testAction("1111"));[b][b]?
数据加工函数[/b][/b]const reducers = {
totalInEuros: (state, item) => {
return state.euros += item.price * 0.897424392;
},
totalInYen: (state, item) => {
return state.yens += item.price * 113.852;
}
};
const manageReducers = reducers => {
return (state, item) => {
return Object.keys(reducers).reduce((nextState, key) => {
reducers[key](state, item);
return state;
}, {})
}
}
const bigTotalPriceReducer = manageReducers(reducers);
const initialState = { euros: 0, yens: 0 };
const items = [{ price: 10 }, { price: 120 }, { price: 1000 }];
const totals = items.reduce(bigTotalPriceReducer, initialState);[b][b]对象空值判断[/b][/b]const get = (p, o) => p.reduce((xs, x) => (xs && xs[x] ? xs[x] : null), o);[b][b]分组[/b][/b]const groupBy = (arr, func) =>
arr.map(typeof func === 'function' ? func : val => val[func]).reduce((acc, val, i) => {
acc[val] = (acc[val] || ).concat(arr);
return acc;
}, {});
groupBy([6.1, 4.2, 6.3], Math.floor);
groupBy(['one', 'two', 'three'], 'length');[b][b]对象过滤[/b][/b]const pick = (obj, arr) =>
arr.reduce((acc, curr) => (curr in obj && (acc[curr] = obj[curr]), acc), {});
pick({ a: 1, b: '2', c: 3 }, ['a', 'c']);[b][b]promise顺序执行[/b][/b]const runPromisesInSeries = ps => ps.reduce((p, next) => p.then(next), Promise.resolve());
const delay = d => new Promise(r => setTimeout(r, d));
const print = args => new Promise(r => r(args));
runPromisesInSeries([() => delay(1000), () => delay(2000), () => print('hello')])[b][b]排序函数[/b][/b]const orderBy = (arr, props, orders) =>
[...arr].sort((a, b) =>
props.reduce((acc, prop, i) => {
if (acc === 0) {
const [p1, p2] = orders && orders === 'desc' ? [b[prop], a[prop]] : [a[prop], b[prop]];
acc = p1 > p2 ? 1 : p1 < p2 ? -1 : 0;
}
return acc;
}, 0)
);
const users = [{ name: 'fred', age: 48 }, { name: 'barney', age: 36 }, { name: 'fly', age: 26 }];
orderBy(users, ['name', 'age'], ['asc', 'desc']);
orderBy(users, ['name', 'age']);[b][b]快速选择器[/b][/b]const select = (from, selector) =>
selector.split('.').reduce((prev, cur) => prev && prev[cur], from);
const obj = { selector: { to: { val: 'val to select' } } };
select(obj, 'selector.to.val'); 查看全部
arr.reduce(callback[, initialValue])reduce为数组中的每一个元素依次执行callback函数,不包括数组中被删除或从未被赋值的元素,接受四个参数:- accumulator
- currentValue
- currentIndex
- array
回调函数第一次执行时,accumulator?和currentValue的取值有两种情况:调用reduce时提供initialValue,accumulator取值为initialValue,currentValue取数组中的第一个值;没有提供?initialValue,accumulator取数组中的第一个值,currentValue取数组中的第二个值
?
计算某个字符出现的次数
[...'abcdaabdcfggtre'].reduce((a,b)=>{a<strong>?a<strong>++:a<strong>=1;return a},{})[b][b]字母游戏[/b][/b]const anagrams = str => {
if (str.length <= 2) {
return str.length === 2 ? [str, str[1] + str[0]] : str;
}
return str.split("").reduce((acc, letter, i) => {
return acc.concat(anagrams(str.slice(0, i) + str.slice(i + 1)).map(val => letter + val));
}, );
}
anagrams("abc");[b][b]累加器[/b][/b]const sum = arr => arr.reduce((acc, val) => acc + val, 0);[b][b]计数器[/b][/b]
sum([1, 2, 3]);
const countOccurrences = (arr, value) => arr.reduce((a, v) => v === value ? a + 1 : a + 0, 0);[b][b]函数柯里化[/b][/b]
countOccurrences([1, 2, 3, 2, 2, 5, 1], 1);
const curry = (fn, arity = fn.length, ...args) =>
arity <= args.length ? fn(...args) : curry.bind(null, fn, arity, ...args);
curry(Math.pow)(2)(10);
curry(Math.min, 3)(10)(50)(2);
[b][b]通过判断函数的参数取得当前函数的length(当然也可以自己指定),如果所传的参数比当前参数少,则继续递归下面,同时储存上一次传递的参数。[/b][/b]
[b][b]数组扁平化[/b][/b]
const deepFlatten = arr =>arr.reduce((a, v) => a.concat(Array.isArray(v) ? deepFlatten(v) : v), );
deepFlatten([1, [2, [3, 4, [5, 6]]]]);
[b][b]生成菲波列契数组[/b][/b]
const fibonacci = n => Array(n).fill(0).reduce((acc, val, i) => acc.concat(i > 1 ? acc[i - 1] + acc[i - 2] : i), );[b][b]pipe函数生成器[/b][/b]
fibonacci(5);
const pipe = (...funcs) => arg => funcs.reduce((acc, func) => func(acc), arg);
pipe(btoa, x => x.toUpperCase())("Test");
[b][b]通过对传递的参数进行函数加工,之后将加工之后的数据作为下一个函数的参数,这样层层传递下去。[/b][/b]
[b][b]compose函数生成器[/b][/b]
const dispatch = action => {
console.log('action', action);
return action;
}
const middleware1 = dispatch => {
return action => {
console.log("middleware1");
const result = dispatch(action);
console.log("after middleware1");
return result;
}
}
const middleware2 = dispatch => {
return action => {
console.log("middleware2");
const result = dispatch(action);
console.log("after middleware2");
return result;
}
}
const middleware3 = dispatch => {
return action => {
console.log("middleware3");
const result = dispatch(action);
console.log("after middleware3");
return result;
}
}
const compose = middlewares => middlewares.reduce((a, b) => args => a(b(args)))
const middlewares = [middleware1, middleware2, middleware3];
const afterDispatch = compose(middlewares)(dispatch);
const testAction = arg => {
return { type: "TEST_ACTION", params: arg };
};
afterDispatch(testAction("1111"));[b][b]?数据加工函数[/b][/b]
const reducers = {
totalInEuros: (state, item) => {
return state.euros += item.price * 0.897424392;
},
totalInYen: (state, item) => {
return state.yens += item.price * 113.852;
}
};
const manageReducers = reducers => {
return (state, item) => {
return Object.keys(reducers).reduce((nextState, key) => {
reducers[key](state, item);
return state;
}, {})
}
}
const bigTotalPriceReducer = manageReducers(reducers);
const initialState = { euros: 0, yens: 0 };
const items = [{ price: 10 }, { price: 120 }, { price: 1000 }];
const totals = items.reduce(bigTotalPriceReducer, initialState);[b][b]对象空值判断[/b][/b]const get = (p, o) => p.reduce((xs, x) => (xs && xs[x] ? xs[x] : null), o);[b][b]分组[/b][/b]
const groupBy = (arr, func) =>[b][b]对象过滤[/b][/b]
arr.map(typeof func === 'function' ? func : val => val[func]).reduce((acc, val, i) => {
acc[val] = (acc[val] || ).concat(arr);
return acc;
}, {});
groupBy([6.1, 4.2, 6.3], Math.floor);
groupBy(['one', 'two', 'three'], 'length');
const pick = (obj, arr) =>[b][b]promise顺序执行[/b][/b]
arr.reduce((acc, curr) => (curr in obj && (acc[curr] = obj[curr]), acc), {});
pick({ a: 1, b: '2', c: 3 }, ['a', 'c']);
const runPromisesInSeries = ps => ps.reduce((p, next) => p.then(next), Promise.resolve());[b][b]排序函数[/b][/b]
const delay = d => new Promise(r => setTimeout(r, d));
const print = args => new Promise(r => r(args));
runPromisesInSeries([() => delay(1000), () => delay(2000), () => print('hello')])
const orderBy = (arr, props, orders) =>[b][b]快速选择器[/b][/b]
[...arr].sort((a, b) =>
props.reduce((acc, prop, i) => {
if (acc === 0) {
const [p1, p2] = orders && orders === 'desc' ? [b[prop], a[prop]] : [a[prop], b[prop]];
acc = p1 > p2 ? 1 : p1 < p2 ? -1 : 0;
}
return acc;
}, 0)
);
const users = [{ name: 'fred', age: 48 }, { name: 'barney', age: 36 }, { name: 'fly', age: 26 }];
orderBy(users, ['name', 'age'], ['asc', 'desc']);
orderBy(users, ['name', 'age']);
const select = (from, selector) =>
selector.split('.').reduce((prev, cur) => prev && prev[cur], from);
const obj = { selector: { to: { val: 'val to select' } } };
select(obj, 'selector.to.val');
JS 线树互转(es6)
每天进步一点点 • lopo1983 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 1742 次浏览 • 2018-07-01 12:09
菜单或者分类等业务场景时,每个顶级节点的parentId约定为0,当存在多个顶级节点,显得不是一个完整的树。所以在这类特殊情况下,我们需要构造一个顶级节点。将菜单或者分类的原有顶级节点存储至该节点的children中。 所以最后约定顶级节点如下。
root = null || {
id: 0,
parentId: null,
children: [node1, node2, ...],
}
线性转树形:function listConvertTree(list) {
let root = null;
if (list && list.length) {
root = { id: 0, parentId: null, children:};
const group = {};
for (let index = 0; index < list.length; index += 1) {
if (list[index].parentId !== null && list[index].parentId !== undefined) {
if (!group[list[index].parentId]) {
group[list[index].parentId] = ;
}
group[list[index].parentId].push(list[index]);
}
}
const queue = ;
queue.push(root);
while (queue.length) {
const node = queue.shift();
node.children = group[node.id] && group[node.id].length ? group[node.id] : null;
if (node.children) {
queue.push(...node.children);
}
}
}
return root;
}树形转线性:function treeConvertList(root) {
const list = ;
if (root) {
const Root = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(root));
const queue = ;
queue.push(Root);
while (queue.length) {
const node = queue.shift();
if (node.children && node.children.length) {
queue.push(...node.children);
}
delete node.children;
if (node.parentId !== null && node.parentId !== undefined) {
list.push(node);
}
}
}
return list;
} 查看全部
菜单或者分类等业务场景时,每个顶级节点的parentId约定为0,当存在多个顶级节点,显得不是一个完整的树。所以在这类特殊情况下,我们需要构造一个顶级节点。将菜单或者分类的原有顶级节点存储至该节点的children中。 所以最后约定顶级节点如下。
root = null || {
id: 0,
parentId: null,
children: [node1, node2, ...],
}
线性转树形:function listConvertTree(list) {
let root = null;
if (list && list.length) {
root = { id: 0, parentId: null, children:};
const group = {};
for (let index = 0; index < list.length; index += 1) {
if (list[index].parentId !== null && list[index].parentId !== undefined) {
if (!group[list[index].parentId]) {
group[list[index].parentId] = ;
}
group[list[index].parentId].push(list[index]);
}
}
const queue = ;
queue.push(root);
while (queue.length) {
const node = queue.shift();
node.children = group[node.id] && group[node.id].length ? group[node.id] : null;
if (node.children) {
queue.push(...node.children);
}
}
}
return root;
}树形转线性:function treeConvertList(root) {
const list = ;
if (root) {
const Root = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(root));
const queue = ;
queue.push(Root);
while (queue.length) {
const node = queue.shift();
if (node.children && node.children.length) {
queue.push(...node.children);
}
delete node.children;
if (node.parentId !== null && node.parentId !== undefined) {
list.push(node);
}
}
}
return list;
} 关于柯里化 curry
每天进步一点点 • lopo1983 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 1713 次浏览 • 2018-06-16 02:37
多亏了ES6,减少了不少阔怕的return,先上李子再扯蛋const add=>(x,y)=>x+y; //一般套路
add(1,2);const addcurry = a=>b=>a+b;//curry套路套路套路
addcurry(1)(2);
// 写下面的代码方便大家理解
var addcurry = function(a){
return function(b){
return b+a
}
}
截图很明显,一下下就明白了,这尼玛就是函数式编程里面的吉娃娃嘛,对 返回的就是一个函数,第一次输入值是返回一个函数,第二次的值作为了他的参数,就是这样 喵!嗷呜。。。。。对了,这里涉及了面试逼问的 闭包!!
是不是觉得 我靠 贼吉尔简单哇!
下面给大家copy 一个最近项目用到的一个李子,这个李子有点酸 是node下面用的?(虽然PHP是世界上最好的语言,总觉得自己可以玩node,结果还是愉快的使用了express-generator,对没错,我的理想还是做一名FBI纪录片摄影记者,侧重点是关注亚麻种植户的疾苦)。但是意思都差球不多 无太多的区别。const client = new AipNlp(...aipconf);
//
const AIPFC = (res) => async(aipfn) => {
const DATA = Object.assign({}, BACKJSON);
let result;
try {
result = await aipfn;
} catch (error) {
result = error
}
res.json(Object.assign(DATA, { data: result })).end();
};
exports.lexer = (req, res) => {
let aipfc = AIPFC(res);
aipfc(client.lexer(req.body.texts));
}前面的废话讲完了 先来说些柯里化 或涉及的一些基础术语
一、一元函数
接收一个参数的函数就叫一元函数(对对对 就是那种绿色的)const fn = (x) => x二、二元函数
接收连个参数的函数就叫二元函数(两张绿色的)const fn = (x,y) = > x+y
三、便餐函数
参数不固定的函数,es6之前用arguments来捕获,es6 可以用结构来获取const fn =(a,...b)=>b.reduce((x,y)=>x+y,a)
这些东西懂的可以忽略或者拍砖 标榜语言不准确的地方,谢谢
很多的函数库里面有会有curry这个函数 比如loash _.curry
下面我简单的来实现一个将多参数 变成一元的函数const add = (a,b)=>a+b;
const curry = (fn)=>(fir)=>(sec)=>fn(fir,sec);
写了那么多东西,你肯定要说,这有屁用啊,屁用都没有,我什么要拆开他,老子的用户都是16核,16G的高端电脑,好好,说个吉娃娃,下面继续李子发起走,我们慢慢的玩上去,来波澳门赌场,澳门皇家赌场开业了。。。。扑哧
假如,我是说假如我们要创建一个列表 有点那么小规律的列表 list2 list3 list4等等
我们先暂时用这来试试const list2 = y=>2*y;
const list3 = y=>3*y;
const list4 = y=>4*y再看看 尼玛 有规律的 来来来 改一版const clist = (a,b)=>a*b;
//
clist(2,2)
clist(2,3)
clist(2,4)
//拿东北的话来说 有一个姓铁的老大爷掉毛了(老铁没毛病);
继续骚起走,李子继续挥泪大甩卖,老板娘除外;const list2 =curry(clist)(2);
const list3 =curry(clist)(3);
const list4 =curry(clist)(4);
console.log(list2(2));
console.log(list2(3));
console.log(list2(4));
console.log(list3(2));
console.log(list3(3));
console.log(list3(4));
console.log(list4(2));
console.log(list4(3));
console.log(list4(4));
查看全部
函数 一等公民 ,越简单的函数越快,把一个复杂的函数打散成多个简单的小函数来执行,能增加执行的速度喝效率,和复用性?。在很多的js大牛的博客上肯定能找到许多的关于这个几把万一二的一些文章喝装13套路的文章,大多数都是互相的复制粘贴之流。简单的说柯里化就是把一个多参函数转换成嵌套的一元函数(毕竟一元最牛逼,因为脸都是绿的)。扯到柯里化 肯定就要继续再扯其他的反柯里化 偏函数 之类的 ,那个以后又空了再装逼。
多亏了ES6,减少了不少阔怕的return,先上李子再扯蛋
const add=>(x,y)=>x+y; //一般套路
add(1,2);
const addcurry = a=>b=>a+b;//curry套路套路套路
addcurry(1)(2);
// 写下面的代码方便大家理解
var addcurry = function(a){
return function(b){
return b+a
}
}
截图很明显,一下下就明白了,这尼玛就是函数式编程里面的吉娃娃嘛,对 返回的就是一个函数,第一次输入值是返回一个函数,第二次的值作为了他的参数,就是这样 喵!嗷呜。。。。。对了,这里涉及了面试逼问的 闭包!!
是不是觉得 我靠 贼吉尔简单哇!
下面给大家copy 一个最近项目用到的一个李子,这个李子有点酸 是node下面用的?(虽然PHP是世界上最好的语言,总觉得自己可以玩node,结果还是愉快的使用了express-generator,对没错,我的理想还是做一名FBI纪录片摄影记者,侧重点是关注亚麻种植户的疾苦)。但是意思都差球不多 无太多的区别。
const client = new AipNlp(...aipconf);前面的废话讲完了 先来说些柯里化 或涉及的一些基础术语
//
const AIPFC = (res) => async(aipfn) => {
const DATA = Object.assign({}, BACKJSON);
let result;
try {
result = await aipfn;
} catch (error) {
result = error
}
res.json(Object.assign(DATA, { data: result })).end();
};
exports.lexer = (req, res) => {
let aipfc = AIPFC(res);
aipfc(client.lexer(req.body.texts));
}
一、一元函数
接收一个参数的函数就叫一元函数(对对对 就是那种绿色的)
const fn = (x) => x二、二元函数
接收连个参数的函数就叫二元函数(两张绿色的)
const fn = (x,y) = > x+y
三、便餐函数
参数不固定的函数,es6之前用arguments来捕获,es6 可以用结构来获取
const fn =(a,...b)=>b.reduce((x,y)=>x+y,a)
这些东西懂的可以忽略或者拍砖 标榜语言不准确的地方,谢谢
很多的函数库里面有会有curry这个函数 比如loash _.curry
下面我简单的来实现一个将多参数 变成一元的函数
const add = (a,b)=>a+b;
const curry = (fn)=>(fir)=>(sec)=>fn(fir,sec);
写了那么多东西,你肯定要说,这有屁用啊,屁用都没有,我什么要拆开他,老子的用户都是16核,16G的高端电脑,好好,说个吉娃娃,下面继续李子发起走,我们慢慢的玩上去,来波澳门赌场,澳门皇家赌场开业了。。。。扑哧
假如,我是说假如我们要创建一个列表 有点那么小规律的列表 list2 list3 list4等等
我们先暂时用这来试试
const list2 = y=>2*y;再看看 尼玛 有规律的 来来来 改一版
const list3 = y=>3*y;
const list4 = y=>4*y
const clist = (a,b)=>a*b;拿东北的话来说 有一个姓铁的老大爷掉毛了(老铁没毛病);
//
clist(2,2)
clist(2,3)
clist(2,4)
//
继续骚起走,李子继续挥泪大甩卖,老板娘除外;
const list2 =curry(clist)(2);
const list3 =curry(clist)(3);
const list4 =curry(clist)(4);
console.log(list2(2));
console.log(list2(3));
console.log(list2(4));
console.log(list3(2));
console.log(list3(3));
console.log(list3(4));
console.log(list4(2));
console.log(list4(3));
console.log(list4(4));
43 位随机码 生成(0~9 A~Z a~z) 可定义位数(位数可随机)
javascript/jQuery • lopo1983 发表了文章 • 2 个评论 • 1466 次浏览 • 2017-04-22 16:20
randomStr: (randomFlag, min, max) => {
let str = "",
range = min,
arr = ['0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z', 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'M', 'N', 'O', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U', 'V', 'W', 'X', 'Y', 'Z'];
if(randomFlag) {
range = Math.round(Math.random() * (max - min)) + min;
}
for(let i = 0; i < range; i++) {
let pos = Math.round(Math.random() * (arr.length - 1));
str += arr[pos];
}
return str;
} 查看全部
//43位随机串 是否指定位数 最小位数 最大位数 (false 43)43位随机
randomStr: (randomFlag, min, max) => {
let str = "",
range = min,
arr = ['0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z', 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'M', 'N', 'O', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U', 'V', 'W', 'X', 'Y', 'Z'];
if(randomFlag) {
range = Math.round(Math.random() * (max - min)) + min;
}
for(let i = 0; i < range; i++) {
let pos = Math.round(Math.random() * (arr.length - 1));
str += arr[pos];
}
return str;
}
vue 滚动到底部
VUE • lopo1983 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 3090 次浏览 • 2017-04-13 03:04
datadata() {
return {
userMsg:
}
}
?
?
methodsgoBottom(e) {
e.scrollTop = e.scrollHeight
}mounted(如果需要进入就滚动)mounted: function() {
this.$nextTick(function() {
let e = this.$refs.chatbox;
this.goBottom(e);
})
}
watch(如果响应)watch: {
userMsg() {
this.$nextTick(() => {
let e = this.$refs.chatbox;
this.goBottom(e);
})
}
}?
?
<-------------------------------------------------邪恶分割线------------------------------------------------>
?
?
以上的代码完全可忽略 因为出现了 邪恶分割线
?
CSS3 FLEX 布局解决display: flex;
flex-flow: column-reverse;
align-items: baseline; 查看全部
<div class="mix" ref="chatbox">....</div>
data
data() {
return {
userMsg:
}
}?
?
methods
goBottom(e) {
e.scrollTop = e.scrollHeight
}mounted(如果需要进入就滚动)mounted: function() {
this.$nextTick(function() {
let e = this.$refs.chatbox;
this.goBottom(e);
})
}watch(如果响应)
watch: {
userMsg() {
this.$nextTick(() => {
let e = this.$refs.chatbox;
this.goBottom(e);
})
}
}??
<-------------------------------------------------邪恶分割线------------------------------------------------>
?
?
以上的代码完全可忽略 因为出现了 邪恶分割线
?
CSS3 FLEX 布局解决
display: flex;
flex-flow: column-reverse;
align-items: baseline;